Recently, clients have shown interest in integrating RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology into optical windshield stickers. This integration enables smarter vehicle traffic management, making vehicle operations more efficient and secure.
Beyond traffic management, RFID technology is used in industries like retail, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, product traceability, access control, and electronic toll collection (ETC).

At our company, we focus on the development and application of RFID technology in access control, ID cards, and vehicle traffic management. Below, we explain RFID technology from five key aspects to help you better understand its potential.
What is RFID Technology?
RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a contactless automatic identification technology that plays a key role in intelligent traffic and vehicle management systems. It uses radio signals to automatically identify moving or stationary objects.
By embedding RFID tags into windshield stickers, vehicles can be automatically identified as they pass through designated reading areas. This enables quick vehicle authentication, automatic toll collection, and efficient tracking.
Components and Working Principles of RFID Systems
An RFID system typically consists of four components: RFID readers, RFID antennas, RFID tags, and a backend system. Communication between RFID readers and tags is facilitated by antennas.
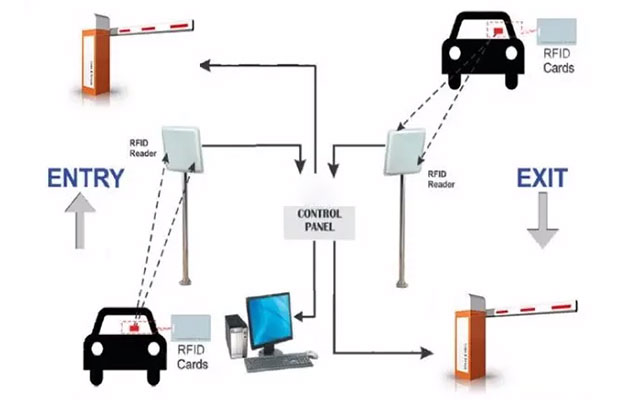
The RFID reader emits radio signals through the antenna to activate the RFID tags, retrieves their information, and decodes it. RFID Antennas facilitate the transmission of radio signals between readers and tags. They are designed according to the frequency band and required reading range.
RFID Tags
RFID tags are made up of three components: the tag body, the chip, and the antenna. There are three main types based on frequency bands:
Low Frequency (LF): Operates at 125 kHz or 134 kHz. LF tags have short reading ranges and limited data capacity, often used in vehicle anti-theft systems and access control.
High Frequency (HF): Operates at 13.56 MHz. HF tags are used in smart cards, identity management, and product tracking systems.
Ultra High Frequency (UHF): Operates at 860–960 MHz, providing a reading range of 3–10 meters. UHF tags can read multiple tags at once, making them ideal for logistics and toll collection systems.
RFID tags also come in two types based on the power source.
Active RFID Tags: These have an internal battery and offer long-range tracking.
Passive RFID Tags: Powered by the reader’s electromagnetic field, they are smaller, lighter, more cost-effective, and longer-lasting.
RFID Readers
RFID readers emit radio waves to communicate with tags via electromagnetic coupling. They use specific communication protocols depending on the frequency band, such as EPCglobal Gen2 for UHF and ISO/IEC 15693 for HF.
RFID Antennas
RFID antennas are sized and shaped according to the frequency band. HF antennas are typically smaller than LF antennas. They can be custom-designed to fit specific application needs using etching or printing techniques.
Backend System
The backend system handles the data collected by RFID readers. It stores, processes, and analyzes this data. It also validates the tag’s ID and compares it with records in a database to trigger appropriate actions.
Applications of RFID Technology in Traffic Management
RFID technology is extensively used in vehicle management, offering benefits such as
Vehicle Identification and Access Control
RFID-enabled windshield stickers streamline vehicle identification at gates, parking lots, and residential complexes. This ensures that only authorized vehicles enter, enhancing both security and efficiency.
Electronic Toll Collection (ETC)
RFID-equipped vehicles can pass through toll gates without stopping. The system communicates with the tag to deduct toll fees automatically, reducing congestion and improving traffic flow.
Intelligent Vehicle Scheduling and Management
Logistics and transportation companies use RFID to track vehicle locations and manage scheduling. By deploying RFID readers in parking lots and depots, they can gather real-time data to optimize vehicle allocation and reduce operational costs.
Anti-theft and Vehicle Tracking
Some anti-theft systems use RFID chips. If a vehicle is started without the correct chip, an alarm is triggered. In case of theft, RFID technology aids in tracking the vehicle’s location.
Vehicle Inspection and Maintenance Management

RFID tags provide quick access to important vehicle information during inspections, such as maintenance records. Repair shops can use RFID to track service logs and send timely reminders for maintenance. Visit vehicle inspection safety stickers for more details.
Vehicle Registration Management
RFID tags act as electronic ID cards for vehicles, linking to detailed registration data, such as the make, model, VIN, and owner. This ensures accurate identification and reduces fraud. Click car windshield registration labels
Future Prospects
The use of RFID technology in the automotive industry has grown to include vehicle tracking, identification, and parking management. These systems are increasingly integrated with smart solutions like automated checkouts at toll stations and parking lots.
In the future, integrating RFID with optical security stickers will likely lead to further innovations in vehicle management. This will improve operational efficiency, enhance security, and provide a better user experience.